If you use the internet, you’re already using AWS. Maybe not directly. But the apps you open, the videos you stream, the files you upload, and the services you depend on every day are very likely running on it and here it is AWS Explained
That’s not hype. That’s just how much ground Amazon Web Services covers.
This post breaks AWS down properly. What it is. What it actually does behind the scenes. Why businesses rely on it. How its current features work. And what AWS is preparing to launch as we move into 2026.
No fluff. No jargon walls. Just a clear explanation you can actually understand.
What Is AWS?
Amazon Web Services, commonly called AWS, is a cloud computing platform that provides on-demand access to computing power, storage, databases, networking, security, analytics, artificial intelligence, and more.
Instead of owning physical servers, companies rent infrastructure from AWS over the internet.
Think of AWS as a global utility for computing. Just like electricity or water, you use what you need, when you need it, and you pay only for what you consume.
AWS launched in 2006. What started as a few internal tools Amazon built for itself turned into the backbone of modern digital business.
Today, AWS runs millions of workloads across startups, governments, enterprises, and everything in between.
Why AWS Exists in the First Place
Here’s the thing. Before cloud computing, running software was painful.
Companies had to:
- Buy servers upfront
- Guess future traffic
- Maintain hardware
- Handle downtime themselves
- Scale slowly and expensively
AWS flipped that model.
Instead of guessing and buying, you provision resources instantly. Instead of worrying about hardware failures, AWS handles the infrastructure. Instead of scaling over months, you scale in seconds.
What this really means is simple. AWS lets businesses focus on building products instead of managing machines.

How AWS Actually Works
At its core, AWS is a massive network of data centers spread across the world.
These data centers are grouped into:
- Regions: Geographic areas like US East, Europe, Asia Pacific
- Availability Zones: Physically separate locations within each region
This design matters because it enables:
- High availability
- Fault tolerance
- Low latency
- Disaster recovery
When you deploy an application on AWS, it doesn’t live on one server in one building. It runs across multiple systems designed to survive failure without users noticing.
Core AWS Services Explained
Let’s break AWS down into its major building blocks.
Compute Services

Compute services are about running code.
Amazon EC2
EC2 provides virtual servers in the cloud. You choose the operating system, CPU, memory, storage, and networking.
Use EC2 when you need:
- Full control over your environment
- Custom software stacks
- Predictable workloads
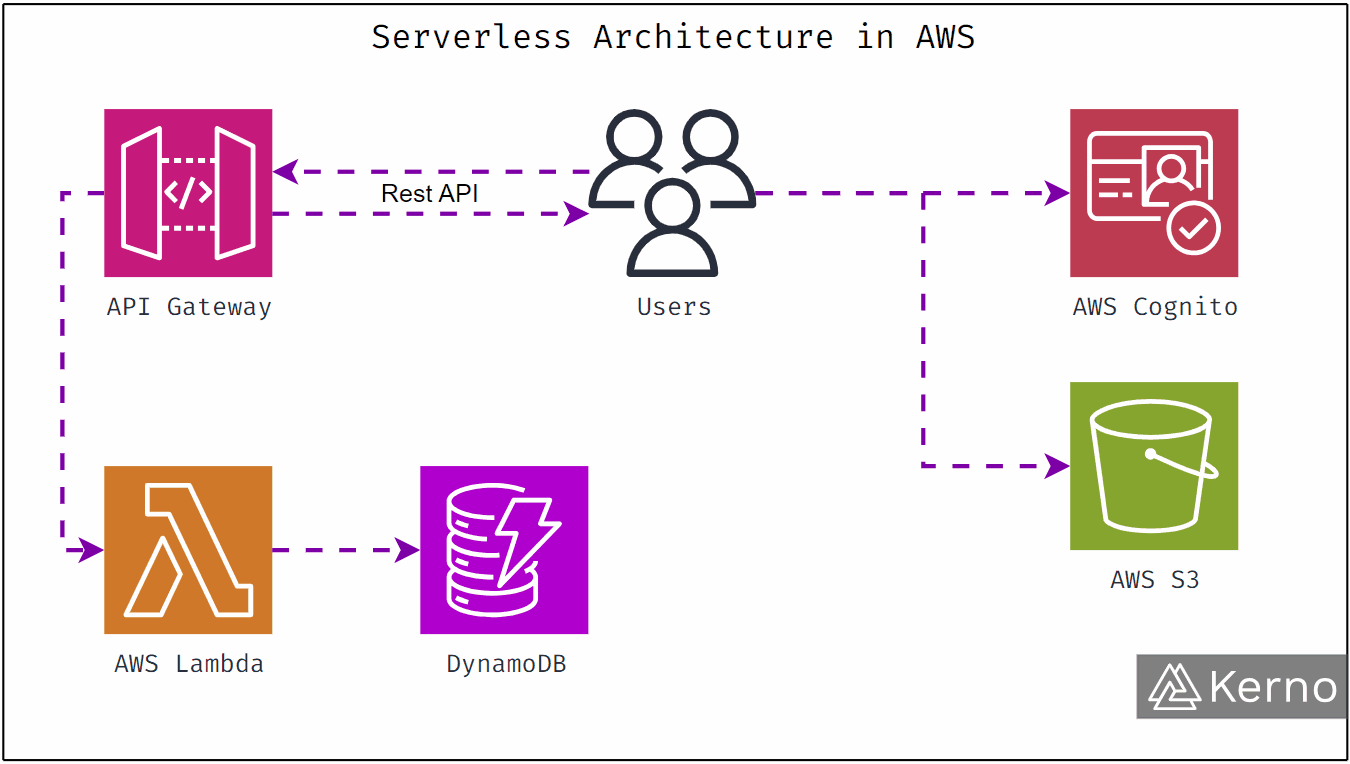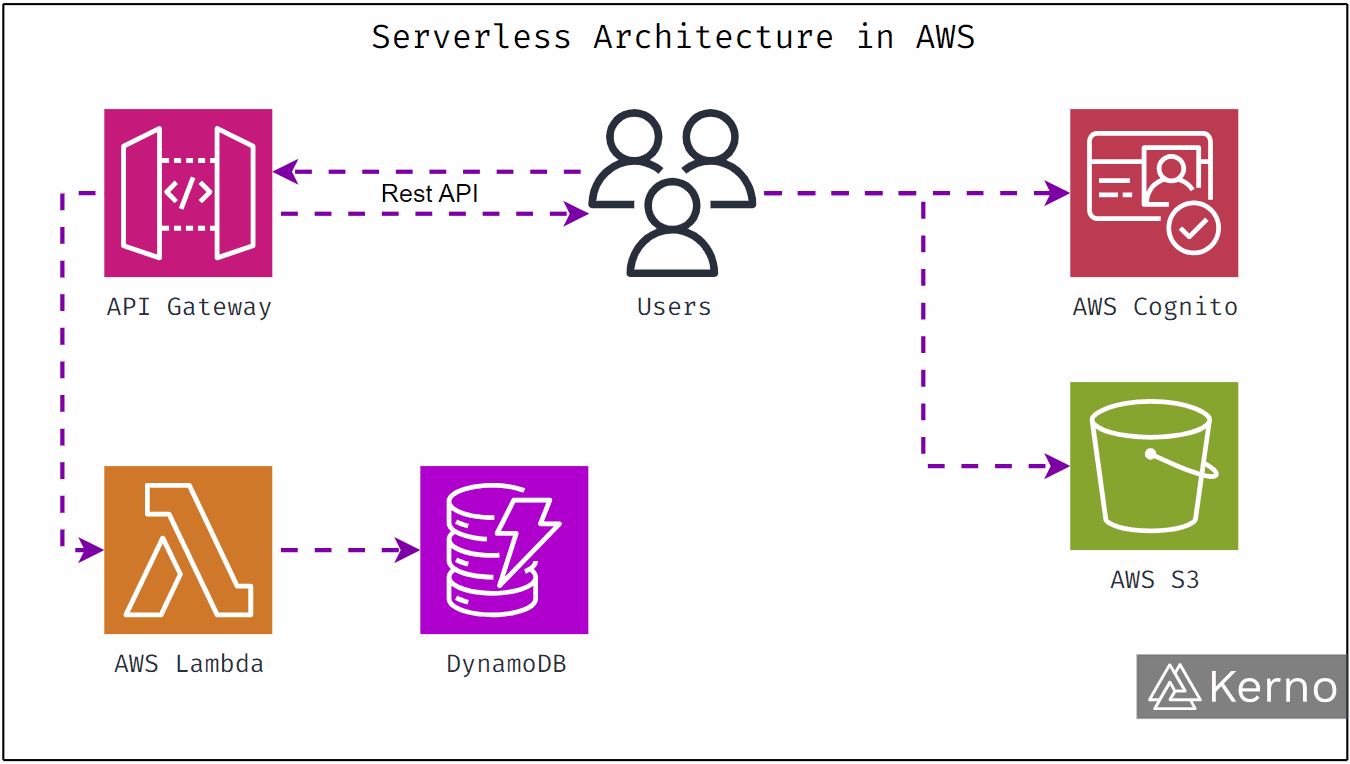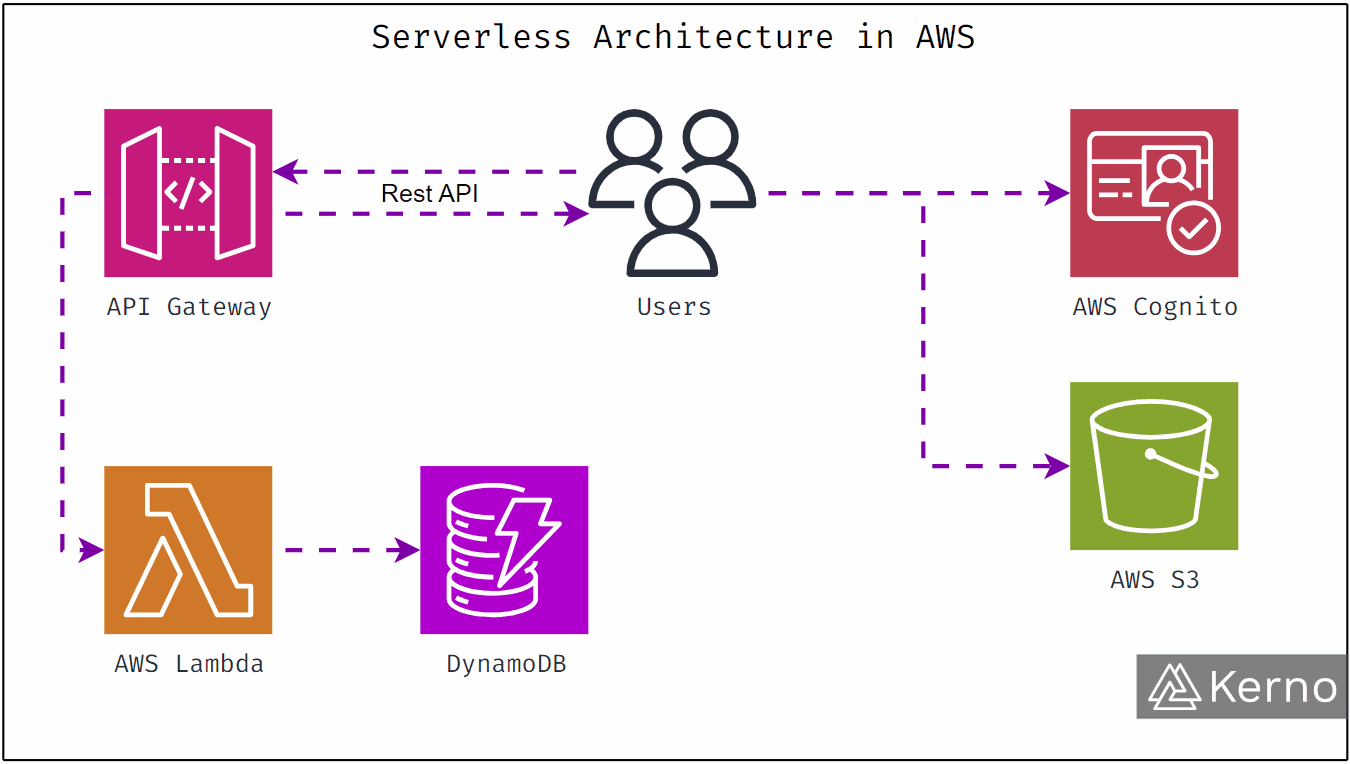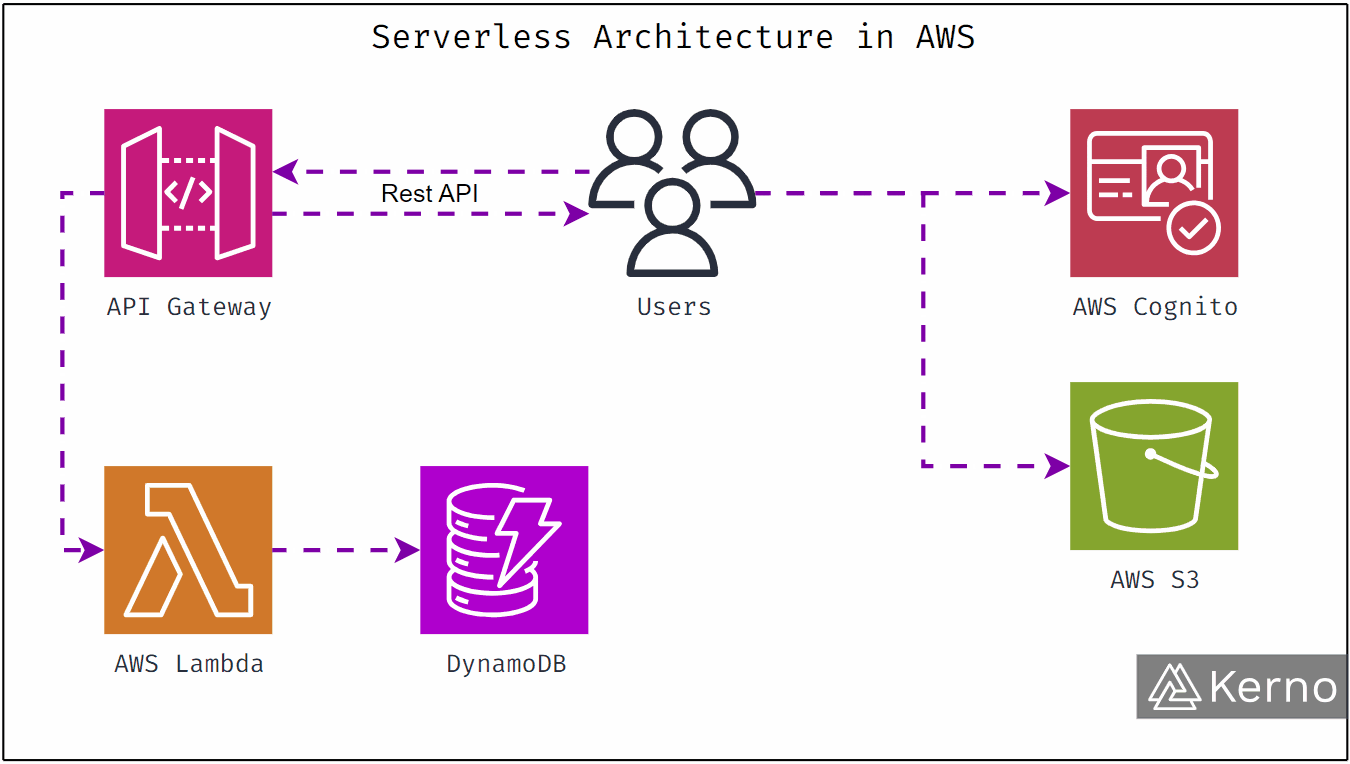
AWS Lambda
Lambda runs your code without servers. You upload functions. AWS runs them automatically when triggered.
This is called serverless computing.
You don’t manage infrastructure. You don’t pay when nothing runs. You only pay per execution.
Elastic Beanstalk
Beanstalk handles deployment, scaling, and monitoring for you. You upload code. AWS manages the rest.
Great for teams that want speed without deep infrastructure work.
Storage Services



Storage is where data lives.
Amazon S3
S3 stores objects like images, videos, backups, and static files.
It’s:
- Highly durable
- Massively scalable
- Globally accessible
S3 is one of the most widely used cloud storage systems on Earth.
Amazon EBS
Elastic Block Store provides storage volumes for EC2 instances. Think of it as cloud hard drives.
Amazon Glacier
Glacier is designed for long-term archival storage. It’s cheap, slow to access, and ideal for compliance and backups.
Database Services
Databases store structured and unstructured data.
Amazon RDS
RDS manages relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
AWS handles:
- Patching
- Backups
- Scaling
- Failover
Amazon DynamoDB
DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database built for massive scale and low latency.
Used when:
- Performance must be consistent
- Data grows unpredictably
- Global access is required
Amazon Aurora
Aurora is a cloud-native relational database built for speed and resilience.
Networking and Content Delivery
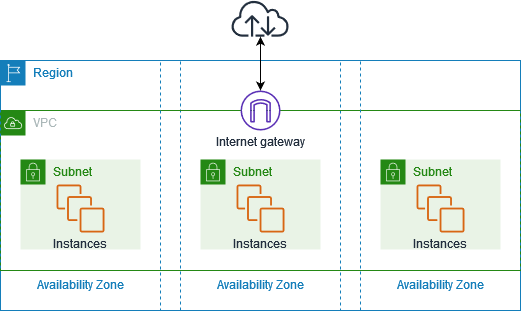


Amazon VPC
VPC lets you create private networks inside AWS. You control IP ranges, routing, and security rules.
Amazon CloudFront
CloudFront is AWS’s content delivery network. It caches content close to users worldwide, reducing latency.
Amazon Route 53
Route 53 handles DNS and traffic routing with high reliability.
Security and Identity
Security is baked into AWS by design.
AWS IAM
Identity and Access Management controls who can access what.
Permissions are granular and auditable.
AWS Shield
Shield protects against DDoS attacks.
AWS KMS
Key Management Service handles encryption keys for secure data protection.
Analytics and Big Data
AWS processes massive data sets.
Amazon Redshift
A data warehouse for analytics at scale.
AWS Glue
ETL service for preparing and moving data.
Amazon Athena
Run SQL queries directly on S3 data without managing servers.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning



AWS offers AI without requiring deep ML expertise.
Amazon SageMaker
Build, train, and deploy machine learning models in one platform.
Amazon Rekognition
Analyze images and videos for faces, objects, and text.
Amazon Comprehend
Natural language processing for text analysis.
DevOps and Automation
AWS supports modern development workflows.
AWS CloudFormation
Infrastructure as code. Define resources using templates.
AWS CodePipeline
Automated CI/CD pipelines.
AWS CloudWatch
Monitoring, logging, and alerting.
What AWS Is Used For in the Real World
AWS powers:
- Streaming platforms
- E-commerce systems
- Financial services
- Healthcare platforms
- Gaming infrastructure
- Government systems
- AI startups
Startups use AWS to move fast. Enterprises use AWS to modernize legacy systems. Governments use AWS for scalability and security.
Different goals. Same platform.
AWS Pricing Explained Simply
AWS pricing is pay-as-you-go.
You pay for:
- Compute time
- Storage used
- Data transferred
- Requests processed
There are no upfront costs unless you choose reserved pricing for discounts.
This model:
- Reduces risk
- Enables experimentation
- Matches cost with usage
Why Businesses Choose AWS Over Others
AWS isn’t the only cloud provider. But it leads for reasons that matter.
- Largest service portfolio
- Deep enterprise adoption
- Global infrastructure
- Mature security model
- Massive ecosystem
- Strong developer tooling
It’s not perfect. But it’s flexible, powerful, and proven at scale.
AWS in 2025: Current Feature Highlights
As of now, AWS focuses on five big themes.
Serverless Expansion
More services support event-driven, serverless architectures.
AI Everywhere
AI capabilities are being embedded into analytics, databases, and developer tools.
Sustainability
AWS continues to invest in energy-efficient data centers and carbon-aware workloads.
Industry-Specific Cloud Solutions
Dedicated offerings for healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
Edge Computing
AWS is pushing compute closer to users with edge services.
What’s Coming Next: AWS Roadmap Toward 2026
While AWS doesn’t reveal everything publicly, patterns are clear.
Here’s where AWS is heading.
1. Smarter AI Infrastructure
AWS is doubling down on custom silicon and optimized AI stacks.
Expect:
- Faster training
- Lower inference costs
- Deeper AI integration across services
AI won’t be a separate product. It’ll be part of everything.
2. More Autonomous Cloud Operations
AWS is moving toward self-healing infrastructure.
This means:
- Automated performance tuning
- Predictive scaling
- Proactive security remediation
Less manual work. Fewer surprises.
3. Simplified Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Support
Businesses don’t want lock-in. AWS knows this.
Expect:
- Better cross-cloud tooling
- Easier on-prem integration
- Unified management layers
4. Developer Experience Overhaul
AWS tools are powerful, but complex.
By 2026, expect:
- Cleaner interfaces
- Smarter defaults
- More opinionated frameworks
- AI-assisted development
Less setup. More building.
5. Industry-Focused AI Models
Instead of generic models, AWS is moving toward domain-specific intelligence.
Think:
- Healthcare diagnostics
- Financial risk analysis
- Manufacturing optimization
- Legal document understanding
6. Quantum and Advanced Computing
Quantum computing won’t be mainstream yet. But AWS will continue expanding research access and simulation capabilities.
This positions AWS for long-term breakthroughs.
AWS Explained for Beginners
If you’re new, here’s the short version.
AWS lets you:
- Build apps without owning servers
- Scale instantly
- Pay only for what you use
- Access advanced tools without massive investment
You don’t need to understand everything on day one. Most teams start small and grow into the platform.
AWS Explained for Businesses
For businesses, AWS means:
- Faster time to market
- Lower infrastructure risk
- Global reach
- Built-in security
- Future-proof architecture
It’s not about technology for its own sake. It’s about agility.
Common Misconceptions About AWS
Let’s clear a few things up.
AWS Is Only for Big Companies
False. Many startups run entirely on AWS.
AWS Is Too Expensive
Only if mismanaged. When used properly, it’s often cheaper than on-prem infrastructure.
AWS Is Insecure
AWS provides strong security controls. Most breaches happen due to configuration errors, not platform flaws.
The Future of AWS Explained Simply
AWS isn’t slowing down.
It’s evolving from infrastructure provider to intelligent platform. One that understands workloads, optimizes itself, and supports innovation at every level.
By 2026, AWS will feel less like a collection of services and more like a cohesive operating system for the cloud.
That’s the direction. And everything AWS is building points there.
Final Thoughts
AWS changed how software is built, deployed, and scaled.
It removed barriers. It reduced risk. It gave builders leverage.
Whether you’re a developer, founder, architect, or decision-maker, understanding AWS isn’t optional anymore.
It’s foundational.
And now, you know exactly why.
Meta Description (160 Characters)
AWS explained in simple terms. Learn what AWS is, how it works, current features, real use cases, and what AWS plans to launch by 2026.
Keywords
AWS explained, what is AWS, Amazon Web Services, AWS cloud computing, AWS services, AWS features, AWS roadmap 2026, AWS future, AWS infrastructure, AWS platform